7 Key Metrics to Optimize Your Go-to-Market Strategy for SaaS Success
7 Key Metrics to Optimize Your Go-to-Market Strategy for SaaS Success
SaaS companies with strong go-to-market (GTM) strategies grow 20-30% faster than their peers. And the secret? Tracking the right metrics.
Metrics like customer acquisition cost and monthly recurring revenue reveal where your strategy works and where it doesn’t.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through the seven key metrics that fuel SaaS growth, helping you build a GTM approach that drives results and scales seamlessly.
What is a Go-to-Market Strategy for SaaS?
A Go-to-Market (GTM) strategy is your game plan for launching a SaaS product and connecting it with your ideal customers. Think of it as your map guiding a product from development to its users.
Why GTM Strategies Matter in SaaS
A strong GTM strategy is the backbone of SaaS growth. It:
- Helps your team identify and understand your target audience
- Clarifies what makes your product unique in the market
- Maps out clear steps to reach and engage your target market
- Converts curious prospects into paying customers
- Increases customer retention, keeping them around for the long term
How Metrics Shape Your GTM Strategy
Your marketing strategy won’t work unless you track key metrics. Metrics like customer acquisition cost (CAC) and churn rate give insight into what’s working and what’s not.
For example:
- CAC: If your CAC is high, your marketing and sales efforts might be too expensive, eating into profits.
- Churn Rate: High churn signals unhappy users. This shows where you can improve the customer experience.
The 7 Most Important Go-to-Market Metrics in SaaS
You need these seven metrics to have a successful SaaS go-to-market strategy.
1. Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)
What is CAC?
Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) is the total cost of acquiring a new customer, including marketing and sales expenses.
For SaaS businesses, understanding CAC helps you measure the efficiency of your marketing and sales efforts.
Why CAC Matters
When CAC is high, you’re spending more to bring in each customer, cutting profits. But when it’s low, your GTM strategy is working efficiently.
In a B2B SaaS environment, an optimal CAC is essential for scalability.
How to Calculate CAC
Calculate CAC by dividing total sales and marketing costs by the number of new customers in a given period:
CAC=Total Sales and Marketing Costs/Number of New Customers

Optimizing CAC: Tips and Examples
Many SaaS companies are adopting Product-Led Growth (PLG) strategies to reduce CAC.
For example, Slack’s free-tier model lets users try the product without upfront costs. The free tier generates leads, which reduces the CAC when they convert to paying customers.
2. Lifetime Value (LTV)
What is LTV?
Lifetime Value (LTV) is the total revenue you expect from customers throughout their time with your company. High LTV indicates loyal customers and strong product-market fit.
Why LTV Matters
LTV tells you if your customer relationships are profitable over time. When paired with CAC, it shows how sustainable your growth is.
For example, if your CAC is higher than your LTV, it’s a red flag—your user acquisition efforts might cost more than they return.
Calculating LTV
Here’s a simple formula for LTV:
LTV=Average Revenue Per User (ARPU)×Average Customer Lifespan
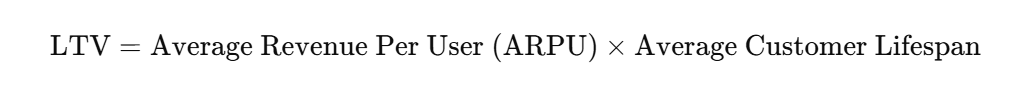
Strategies to Boost LTV
- Customer Retention Programs: Keeping existing customers happy costs less than acquiring new ones. Companies like HubSpot use customer success teams to retain clients.
- Upsell and Cross-sell: Offering upgrades or complementary products to existing customers is another way to increase LTV.
3. Churn Rate
What is the Churn Rate?
The churn rate measures the percentage of customers canceling their subscriptions over a period. A high churn rate signals potential issues with product satisfaction or support.
Why Churn Rate is Critical
Reducing churn is crucial for sustainable SaaS growth.
For example, if 20% of your customers leave annually, you must continuously acquire new customers to maintain revenue, which increases CAC.
Calculating Churn Rate
To calculate the churn rate, divide the number of lost customers by the total customers at the beginning of the period:
Churn Rate=Number of Customers Lost/Total Customers at Start×100
Tips to Minimize Churn
- Improve Onboarding: Make it easy for new customers to get started with your product.
- Regular Check-ins: Customer support teams can spot issues early and prevent churn.
- Collect Customer Feedback: Use exit surveys to understand why customers leave and address common issues.
4. Net Promoter Score (NPS)
What is NPS?
Net Promoter Score (NPS) is a customer loyalty metric gauges how likely customers are to recommend your product. Higher scores indicate satisfied customers who can drive organic growth through referrals.
Why NPS is Essential
In B2B SaaS, NPS can indicate customer satisfaction and loyalty. A low NPS might suggest areas for improvement.
For example, if enterprise clients aren’t happy, they won’t renew or expand their contracts.
How to Calculate NPS
Ask customers, “On a scale of 1 to 10, how likely are you to recommend us to a friend?” Then, categorize responses:
- Promoters (score 9-10): Loyal, likely to recommend
- Passives (score 7-8): Neutral
- Detractors (score 0-6): Unhappy, unlikely to recommend
Increasing NPS
- Improve Customer Support: Fast, practical support can turn detractors into promoters.
- Engage with Feedback: Show customers you’re listening by implementing changes based on their suggestions.
5. Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR) and Annual Recurring Revenue (ARR)
What are MRR and ARR?
MRR is the monthly predictable revenue from subscriptions, while ARR is the yearly equivalent. Both metrics offer insight into revenue stability.
Why MRR and ARR Matter
These metrics help you track growth and make revenue forecasts. B2B SaaS companies use ARR to gauge annual performance, often a more stable view of revenue for long-term planning.
How to Track MRR and ARR
Calculate MRR by adding up all subscription revenue from your customers in a month. ARR is simply MRR multiplied by 12.
ARR=MRR×12
Boosting MRR and ARR
- Upsell Existing Customers: Offer add-ons that add value.
- Reduce Discounting: Avoid over-relying on discounts to keep pricing models strong and protect MRR.
6. Sales Cycle Length
What is the Sales Cycle Length?
Sales cycle length measures the time it takes from first contact with a lead to closing the sale. Shortening this cycle can improve revenue generation.
Why Sales Cycle Length is Important
For B2B SaaS, long sales cycles mean delayed revenue. Companies selling enterprise solutions often have longer cycles due to decision-making layers, while shorter cycles indicate efficient sales processes.
How to Measure Sales Cycle Length
Track the average time it takes to convert leads to customers. Depending on the product, this could be days, weeks, or months.
Ways to Optimize Sales Cycle Length
- Streamline Sales Processes: Tools like CRM software can reduce administrative tasks.
- Target High-Intent Leads: Prioritize leads with clear buying intent to shorten the cycle.
7. Lead-to-Customer Conversion Rate
What is the Conversion Rate?
The lead-to-customer conversion rate measures the percentage of leads that turn into paying customers. A high conversion rate shows your GTM strategy effectively moves leads through the sales funnel.
Why Conversion Rate is Crucial
Tracking this rate helps assess the effectiveness of your GTM strategy. If it’s low, it may indicate weak messaging or inefficient sales processes.
Calculating Conversion Rate
To find the conversion rate, divide the number of converted leads by the total number of leads:
Conversion Rate=Leads Converted to Customers/Total Leads×100
Ways to Improve Conversion Rate
- Refine Targeting: Focus on your ideal customer profile.
- Optimize Touchpoints: Engage leads with valuable content through email marketing and social media.
- Improve Sales-Ready Messaging: Tailor messaging to address customer pain points directly.
Integrating Metrics into Your SaaS GTM Strategy
Monitoring these metrics is only the first step. Using them to guide your marketing strategy is where you’ll see results.
Here’s how to make the most of them.
Best Practices for Using Metrics in GTM
When you integrate metrics, focus on these key practices:
- Set Clear Goals for Each Metric
Every metric should have a purpose. If you’re tracking CAC, set a target CAC for which to aim. This helps marketing teams know if they’re attracting leads cost-effectively. - Track Key Metrics Regularly
Regularly monitoring metrics like churn rate and MRR shows you how your strategy works in real-time. For example, HubSpot tracks these monthly to align with growth goals and adjust quickly if any red flags arise. - Analyze Trends, Not Just Numbers
Metrics tell a story over time. If your churn rate rises, it could signal product or customer service issues. Noticing this trend lets you act before the problem grows.
Regular Tracking and Analysis
Tracking isn’t a one-time job. Here’s why regular checks are crucial:
- Spot Patterns Early
Monthly or quarterly checks on metrics like lead conversion rates and MRR reveal shifts early. If lead conversions drop, it may be time to review messaging or target a new customer segment. - Benchmark Against Competitors
Compare your metrics with industry standards. If competitors achieve a lower CAC, it might be time to review your marketing channels or improve targeting.
Adapt Your GTM Strategy Based on Insights
Metrics offer valuable insights, but only if you’re willing to adapt:
- Revamp Strategies Based on Data
If CAC is high, explore organic channels like content marketing or leveraging customer referrals to lower costs. For example, Dropbox famously used referral programs to reduce CAC while growing its user base. - Improve Customer Experience for Retention
High churn rates could mean customers aren’t satisfied with the onboarding or support. Many SaaS companies, like Intercom, use churn data to improve customer success programs and keep individual users engaged in the long term.
Conclusion
Now, you have a clear idea of the key metrics that shape a strong go-to-market strategy for SaaS. Tracking CAC, LTV, churn rate, and more lets you see what’s working and needs a tweak.
Remember, each metric adds insight—use it to adjust your approach and keep your strategy on track.
If you’re ready for expert help in building a data-driven go-to-market plan that grows with your business, Aventi Group can help. Contact us to create a killer strategy built for SaaS success.




